Before going into the details of computing outer probabilities we describe their use in obtaining the expected rule counts needed for the E-step in grammar estimation.
Let ![]() denote the expected number of uses of
production
denote the expected number of uses of
production ![]() in the derivation of string x.
Alternatively,
in the derivation of string x.
Alternatively, ![]() is the expected
number of times that
is the expected
number of times that ![]() is used for prediction in a complete Earley path generating x.
Let
is used for prediction in a complete Earley path generating x.
Let ![]() be the number of occurrences of predicted states
based on production
be the number of occurrences of predicted states
based on production ![]() along a path
along a path ![]() .
.
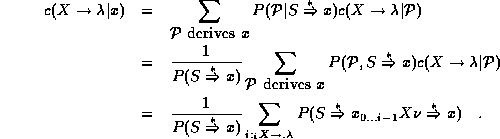
The last summation is over all predicted states based on production
![]() .
The quantity
.
The quantity ![]() is the sum of the probabilities of all paths
passing through
is the sum of the probabilities of all paths
passing through ![]() .
Inner and outer probabilities have been defined such that this
quantity is obtained precisely as the
product of the corresponding of
.
Inner and outer probabilities have been defined such that this
quantity is obtained precisely as the
product of the corresponding of ![]() and
and ![]() .
Thus, the expected usage count for a rule can be computed as
.
Thus, the expected usage count for a rule can be computed as
![]()
The sum can be computed after completing both forward and backward passes (or during the backward pass itself) by scanning the chart for predicted states.